The gut communicates with the brain through neural, endocrine, and immune pathways, a connection often referred to as the “second brain.” This system relies on the vagus nerve, microbial metabolites, and immune messengers to regulate stress response, mood, and cognition.
connection often referred to as the “second brain.” This system relies on the vagus nerve, microbial metabolites, and immune messengers to regulate stress response, mood, and cognition.
Recent studies show that up to 95% of the body’s serotonin is produced in the gut, where microbes help synthesize and modulate neurotransmitters such as dopamine, GABA, and acetylcholine. Dysbiosis, inflammation, and/or intestinal permeability can disrupt this signaling, contributing to anxiety, depression, and cognitive decline.
The gut–brain axis has also been linked to disorders like IBS, chronic fatigue, and mood instability, where immune activation and microbial imbalance play key roles. Functional testing allows providers to map these interactions and design targeted interventions for improved emotional and neurological health.
Inside the Gut Zoomer: Mapping the Microbial Network

The Vibrant Gut Zoomer brings the gut ecosystem into focus with a stool-based profile of 200+ microbes (commensals, opportunists, pathogens) plus integrated readouts of inflammation, barrier integrity, digestion and malabsorption, gut antibodies, and microbial metabolites. The result is a single, comprehensive snapshot that helps explain microbiome balance and its potential links to stubborn GI and gut–brain symptoms.
Functional Insights Include:
- Neurological Health: Identifies gut bacteria associated with neurotransmitter production, such as Bifidobacterium longum, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, and Akkermansia muciniphila.
- Inflammation and Immune Activation: Measures markers like calprotectin, beta-defensin 2, and S100A12, revealing mucosal inflammation linked to brain fog and mood symptoms.
- Digestion and Immune Balance: Evaluates pancreatic elastase, fecal zonulin, and secretory IgA to assess digestion and intestinal barrier integrity.
- Metabolites and Diversity: Quantifies beta-glucuronidase, bile acids, short-chain fatty acids (acetate, butyrate, propionate) and diversity indices like Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio to measure gut ecosystem balance.
By integrating microbial, inflammatory, and metabolic data, the Gut Zoomer uncovers how microbial imbalances may influence brain health through immune, endocrine, and metabolic pathways.
Inside the Neurotransmitters Panel: Measuring Chemical Messengers
The Vibrant Neurotransmitters Panel is a urine-based look at neurochemistry that brings the essentials into one view, inhibitory tone, excitatory drive, and pathway context via key metabolites and ratios. It also includes a four-point diurnal catecholamine series to reveal day–night stress patterns and inform timing for support. Taken together, it provides a concise map of tone, turnover, and timing that supports evaluation of mixed mood, sleep, energy, and focus concerns.
Functional Insights Include: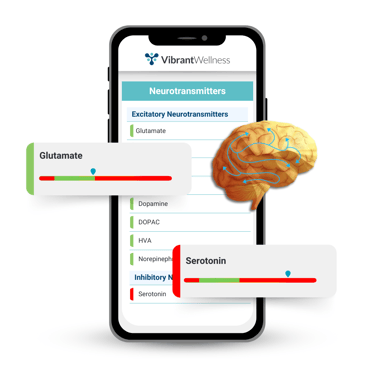
- Excitatory Neurotransmitters: Dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine, glutamate, and histamine, critical for motivation, alertness, and focus.
- Inhibitory Neurotransmitters: Serotonin, GABA, glycine, and taurine — vital for mood stability, calm, and restorative sleep.
- Metabolites and Ratios: Includes HVA/DOPAC (dopamine turnover), Quinolinic acid/5-HIAA (neuroinflammatory balance), and Norepinephrine/Epinephrine (stress response regulation)
- Diurnal Profiles: Measures morning, afternoon, and evening norepinephrine and epinephrine levels to reveal circadian rhythm patterns.
These results help providers identify biochemical patterns associated with anxiety features, low motivation, brain fog, sleep disturbances, and mood variability, offering a structured view of neurochemical balance that can support evaluation and care planning.
Why Test Both? Bridging Microbiome Data with Neurochemical Function
The Gut Zoomer + Neurotransmitters Bundle views the gut–brain axis from both ends of the communication loop. Gut Zoomer highlights how microbial imbalance, inflammation, barrier stress, and digestive insufficiency may disrupt neurotransmitter synthesis and signaling. The Neurotransmitters Panel then shows how those upstream issues may manifest as inhibitory/excitatory imbalance, pathway bottlenecks (via metabolites/ratios), and day–night stress-pattern shifts. Seen together, they turn broad symptom lists into staged, mechanism-based care.
How the pieces fit
- Mechanism → Mediator: Low SCFAs (e.g., butyrate), barrier stress (e.g., zonulin), or mucosal inflammation can be associated with altered serotonin/GABA tone or tryptophan routing toward kynurenine/quinolinic acid pathways.
- Mediator → Mechanism: Diurnal catecholamines and key ratios (HVA/DOPAC, NE/Epi, Quinolinic acid/5-HIAA) help distinguish hyperarousal vs. flattened stress tone and guide the timing of support while gut repair proceeds.
- Clinical payoff: Dual testing reduces trial-and-error, clarifies what to address first, and aligns gut stabilization, ecosystem rebuilding, and cofactor support with targeted neurochemical adjustments.
Example: Dysbiosis with elevated β-glucuronidase and low butyrate may promote inflammation and hormone recirculation, which can correlate with lower serotonin or dopamine output. Running both panels clarifies where these mechanisms overlap and where to intervene.
Clinical Applications: Translating Data into Personalized Care

Providers can use bundle insights to design targeted treatment plans that integrate gut restoration with neurochemical rebalancing:
- Support microbial diversity: Add targeted prebiotic fibers and indicated strains (e.g., Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus) when commensal balance/diversity are low.
- Reduce inflammation & protect the barrier: If calprotectin, S100A12, or zonulin are elevated, prioritize gut-directed anti-inflammatory strategies and barrier support before stimulating pathways.
- Optimize neurotransmitter pathways: Use ratios (HVA/DOPAC, NE/Epi, Quinolinic acid/5-HIAA) and precursor insights (e.g., tryptophan, tyrosine, GABA analogs as appropriate) to fine-tune tone once gut foundations are set.
- Modulate the stress response: Time calming vs. resilience-building interventions using diurnal catecholamine patterns to align support with day–night dynamics.
This integrated model links symptoms (e.g., brain fog, irritability, fatigue) to objective findings and supports evaluation and staged care planning, improving patient engagement and long-term outcomes.
The Bottom Line
The Gut–Brain Axis Bundle unites two complementary perspectives, gut mechanisms (microbiome, inflammation, barrier, digestion, metabolites) and neurochemical mediators (inhibitory/excitatory tone, metabolites, ratios, diurnal catecholamines) into one clinically actionable package. By connecting microbial health with neurotransmitter balance, it helps providers uncover the why behind mood features, cognitive changes, and stress dysregulation and translate findings into clear, sequence-based care.
(microbiome, inflammation, barrier, digestion, metabolites) and neurochemical mediators (inhibitory/excitatory tone, metabolites, ratios, diurnal catecholamines) into one clinically actionable package. By connecting microbial health with neurotransmitter balance, it helps providers uncover the why behind mood features, cognitive changes, and stress dysregulation and translate findings into clear, sequence-based care.
Available now: The Gut–Brain Axis Bundle, Gut Zoomer + Neurotransmitters Panel is live in your provider portal. Order today to begin offering a compelling, single-story readout of the gut–brain axis and experience our most comprehensive approach to gut–brain testing.
Order the Gut–Brain Axis Bundle in your provider portal to start delivering a clearer, mechanism-driven plan for your patients.

Regulatory Statement:
The general wellness test intended uses relate to sustaining or offering general improvement to functions associated with a general state of health while making reference to diseases or conditions. This test has been laboratory developed and its performance characteristics determined by Vibrant America LLC and Vibrant Genomics, a CLIA-certified and CAP-accredited laboratory performing the test. The lab tests referenced have not been cleared or approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Although FDA does not currently clear or approve laboratory-developed tests in the U.S., certification of the laboratory is required under CLIA to ensure the quality and validity of the tests
 (microbiome, inflammation, barrier, digestion, metabolites) and neurochemical mediators (inhibitory/excitatory tone, metabolites, ratios, diurnal catecholamines) into one clinically actionable package. By connecting microbial health with neurotransmitter balance, it helps providers uncover the why behind mood features, cognitive changes, and stress dysregulation and translate findings into clear, sequence-based care.
(microbiome, inflammation, barrier, digestion, metabolites) and neurochemical mediators (inhibitory/excitatory tone, metabolites, ratios, diurnal catecholamines) into one clinically actionable package. By connecting microbial health with neurotransmitter balance, it helps providers uncover the why behind mood features, cognitive changes, and stress dysregulation and translate findings into clear, sequence-based care. connection often referred to as the “second brain.” This system relies on the vagus nerve, microbial metabolites, and immune messengers to regulate stress response, mood, and cognition.
connection often referred to as the “second brain.” This system relies on the vagus nerve, microbial metabolites, and immune messengers to regulate stress response, mood, and cognition.











